Any automotive diagnostics protocol such as OBD2 / UDS / KWP work on a request – response basis. External Tester sends a request to ECU and the ECU sends back a response to tester. Now, the ECU can send a positive response corresponding to the request or can send a negative response based on several criteria.
A positive response from an ECU always starts with the first byte having Request ID (HEX) + 0x40. Find below some examples of positive response from the ECU.
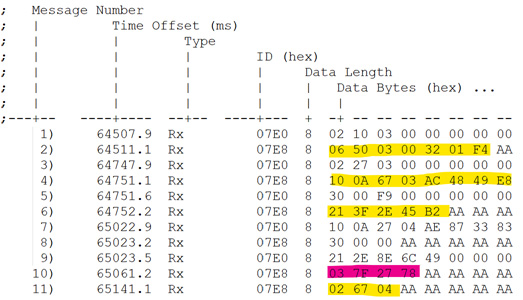
In the log above, 7E0 is the tester Tx ID, 7E8 is the ECU Tx ID Responses in yellow are positive responses.
A negative response from an ECU always starts with the first byte having 0x7F followed by the second byte having request ID followed by third byte having the Negative response code (NACK Code / NRC). This negative response code indicates the reason for the negative response.
There is however a special negative response with NRC 0x78 which is sent by the ECU to keep the external tester on hold to receive a subsequent response (which may be a positive / negative response). In the above log, see the response in Pink for reference.
NRC Table
All the negative response codes are split into three categorized from 0x00 – 0xFF ranges, such as:
1. 0x00: positive response parameter value for server internal implementation.
2. 0x01 – 0x7F: communication-related negative response codes.
3. 0x80 – 0xFF: NRC indicating specific conditions that are not correct at that instant of time when the request is received by the server. These response codes could also be utilized whenever the response code 0x22 is listed as valid. By the way to report more specifically why the requested action cannot be taken for a positive response.
| NRC Code Value | NRC Code Name | Description |
| 0x00 | Positive Response | The 0x00 is a special and initiative value that cannot be used for ant NRC. It is this parameter value reserved for several internal code implementation reason. |
| 0x01 – 0x0F | ISO SAE Reserved | This range of NRC is reserved for the future definition that maybe increase the diagnostic functionality more. |
| 0x10 | General Reject | If there is none of the NRC is available in UDS standard document to meet the needs of the implementation, then you can use this NRC for your ECU. |
| 0x11 | Service Not Supported | Suppose the client has sent a request with a Service Identifier. That is not supporting in your ECU by your OEM. Even if you can also say as per the requirement or as per the OEM. But the service engineer or client has requested that unknown SID request to the server. Then the server will send the 0x11 NRC response message to the client that it is an unknown Service Identifier. |
| 0x12 | Sub-function Not Supported | Suppose the client has sent a valid and known Service identifier. But the Sub-function Identifier is unknown or invalid. then the server will send 0x12 Negative Response Code to the client. |
| 0x13 | Incorrect Message Length Or Invalid Format | If the client has sent any diagnostic request message whose length or the frame format does not match with the prescribed length or the format for that specified service (SID), then the server will send this NRC. |
| 0x14 | Response Too Long | If the client has sent a diagnostic request and the response message length is more than the Transport protocol maximum length, then the server will send this NRC. The CAN-TP has 4096 bytes has a maximum length, if the server will send more than that, then this NRC will be sent by the server to the client. Ex: suppose you requested more number of DIDs at a time to read the data if it will cross that limit, then this NRC will get generated by the server. |
| 0x15 – 0x20 | ISO SAE Reserved | This range of NRC is also reserved for the future definition that maybe increase the diagnostic functionality more. |
| 0x21 | Busy Repeat Request | If the server is too busy with some other operation or you can say any other client request in a multi-client environment, then the server will send this NRC to the client. This NRC is supported by each SID. Ex: Suppose there are two clients connected to your vehicle simultaneously. One client has already requested a service that is under process means incomplete and the second client is requesting another request to the server then the server will send the NRC 0x21 to the second server to wait for some time. This time will be defined in the document that you need to check. |
| 0x22 | Conditions Not Correct | Before proceeding any service from the client, the server will check for prerequisite conditions are met or not. If not then the server will send this NRC. Ex: you can say the ECU operational low threshold or high threshold voltage, temperature, etc. |
| 0x23 | ISO SAE Reserved | This NRC is also reserved for the future definition. |
| 0x24 | Request Sequence Error | If the client will send the diagnostic message non-sequentially, then the server will send this NRC to the client. Ex: Suppose in security access SID, the client sent security key first and then seed request, then the server will send this NRC. because in this 0x27 service, the client should send the seed request first and then the security key. |
| 0x25 | No Response From Sub-net Component | Suppose the diagnostic request service sent by the client to the server, but the received ECU is not the target ECU and it is a gateway. So that the Gateway ECU will send this request to the target ECU and that should perform the operation and send back the response message to the Gateway ECU, and then it will send the response message. If the Gateway ECU does not receive the response message from that target ECU or server then the Gateway ECU will send this NRC to the client. This NRC supported by each SID. |
| 0x26 | Failure Prevents Execution Of Requested Action | If the client requested service and at that time a fault occurred in server ECU after receiving of this ECU so that at least one DTC status bit for TestFailed, Pending, Confirmed or TestFailedSinceLastClear set to 1, then the server will send this NRC to the client. Basically this failure condition prevents the server from performing the requested action so that the server will not able to execute the client request. |
| 0x27 – 0x30 | ISO SAE Reserved | This NRC is also reserved for the future definition. |
| 0x31 | Request Out Of Range | If the server received a client request with a parameter (DID, RID) that is out of range, then the server will send this NRC. Suppose in your ECU, the DID or RID having some range used and the client requesting it which is not supported in your ECU or might be not supported in this active session, it will send this NRC. |
| 0x32 | ISO SAE Reserved | This NRC is also reserved for the future definition. |
| 0x33 | Security Access Denied | The server will send this NRC if the security strategy is not satisfied with the server. The Server will send this NRC if any of the below conditions will not satisfy: Server test conditions are not met. Service message sequence (first diagnostic session and then security access service request). The server needs to unlock by the client for some read or write access to the server, but without unlock, a client trying to access the protected memory. |
| 0x34 | ISO SAE Reserved | This NRC is also reserved for the future definition. |
| 0x35 | Invalid Key | If the server received a security key from the client that is not matching with the server-generated key, then the server will send this NRC. |
| 0x36 | exceed Number Of Attempts | Basically, in each server, there will be a security retrieval counter and it will be having a limit like 3 or 5 times. So if a client will send the wrong security key more than the defined counter value, the server will send this NRC to the client. |
| 0x37 | Required Time Delay Not Expired | Once the client will send a wrong security key, client should wait the defined time, and then it should send the key again. But if the client will send the security key before that then the server will send this NRC. |
| 0x38 – 0x4F | Reserved By Extended Data Link Security Document | This is reserved for future implementation of security layer related NRC |
| 0x50 – 0x6F | ISO SAE Reserved | This NRC is also reserved for the future definition. |
| 0x70 | Upload Download Not Accepted | Sometimes due to some fault conditions in the server or server memory, it will not accept any upload or download request from the client. |
| 0x71 | Transfer Data Suspended | During the data transfer, sometimes due to some failure of any kind of fault, the server will not able to write data onto the memory. So in that situation, the server will send this NRC to the client. |
| 0x72 | General Programming Failure | If the server detects an error during the erasing or programming of the memory location of permanent memory (e.g., NVM/Flash/EEPROM), then the server will send this NRC to the client. |
| 0x73 | Wrong Block Sequence Counter | Basically, whenever a multi-frame consecutive data packet sent by the client to server. In the Consecutive Frame, there will be a Frame index that will increase in each next frame. The server also receives that and compares it with the previous value that should be +1 in each current frame received. If there is any miss match, the server will send this NRC to the client. |
| 0x74 – 0x77 | ISO SAE Reserved | This NRC is also reserved for the future definition. |
| 0x78 | Request Correctly Received-Response Pending | This NRC indicates that the request message from client successfully received by the server. All the requested parameters are also valid. But the server is not ready or due to busy or it is taking some more time to execute the client request in the defined server parameter. So if the client sends another request or the server P2 Client time out happened, the server will send this NRC to the client to inform that to wait for some more time period nothing but the P2* Client timing value. After the execution, the server will send either a positive or negative response message. |
| 0x79 – 0x7D | ISO SAE Reserved | This NRC is also reserved for the future definition. |
| 0x7E | Sub-function Not Supported In Active Session | This NRC will return by the server if the requested sub-function Identifier is not supported in this session. basically, in UDS protocol there are 3 sessions. In each session what services and their sub-functions will support it will be decided by the OEM. If the tester will request a service with a correct subfunction for this service Identifier but that is not supported in this session, then obviously the server will send this NRC to the client. But remember there might be a possibility that the same sub-function and service Identifier will support in any other session. |
| 0x7F | Service Not Supported In Active Session | This NRC will return by the server if the requested service identifier is not supported in this session. |
| 0x80 | ISO SAE Reserved | This NRC is also reserved for future definition. |
| 0x94 – 0xEF | Reserved For Specific Conditions Not Correct | |
| 0xF0 – 0xFE | Vehicle Manufacturer Specific Conditions Not Correct | |
| 0xFF | ISO SAE Reserved |
For more information about the NRC and other aspects of automotive diagnostics and to practically learn this topic, you are welcome to subscribe to our YouTube channel or book for a training session on Automotive Diagnostics.
